We've all been there: you start watching a video—whether it's a new release on YouTube, a low-bitrate live stream, or an older local video file—only to find the content is marred by frustratingly low resolution, noticeable compression artifacts, and general blurriness when scaled up to your high-resolution monitor. A significant amount of video content, both online and in your personal library, still falls short of modern high-definition quality.
Fortunately, a revolutionary solution is available for users of modern NVIDIA graphics cards. Enter NVIDIA RTX Video Super Resolution (VSR), an AI-powered technology that harnesses the Tensor Cores in RTX GPUs to instantly and dramatically upgrade the quality of video streaming and playback in real-time.
This comprehensive guide is your deep dive into the world of VSR. We will unpack how this AI magic works, provide a simple step-by-step tutorial on how to activate and optimize it, address the most common performance and troubleshooting questions, and objectively review its capabilities and limitations. Prepare to transform your digital viewing experience.
💡 If you need to actually save or restore your videos
RTX Video Enhancement is great for real-time viewing, but its improvements are temporary — you can’t save or archive the enhanced result.
If you need permanent upscaling or restoration for editing or preservation, you’ll need a dedicated AI tool like Aiarty Video Enhancer. It can upscale up to 4K, sharpen soft footage, reduce noise, fix pixelation, boost fps, convert SDR to HDR, and export a fully improved file you can keep.
Download Aiarty Video Enhancer to enhance and upscale your videos:
If you're curious to see how Aiarty Video Enhancer performs in action, check out the hands-on test video below.
Core Technology: Unpacking RTX Video Enhancement (VSR & HDR)
NVIDIA's RTX Video Enhancement is not a single feature, but a suite of AI-driven tools designed to radically improve the quality of video streaming and playback in real-time. This suite is powered by the specialized Tensor Cores found in modern GeForce RTX graphics cards, allowing sophisticated deep learning models to run instantaneously as you watch.
This section covers the two primary functions of this technology suite:
A.RTX Video Super Resolution (VSR)
VSR is the foundational component, addressing the issues of low-resolution and high compression common in video content, whether local or streaming.
Traditional upscaling simply stretches pixels, leading to blurriness and blockiness. VSR uses an AI model trained on thousands of videos to analyze multiple low-resolution frames and predict the genuine details and textures that are missing. This allows it to generate a higher-resolution image with significantly greater fidelity.
VSR performs two essential, simultaneous tasks:
- Intelligent Resolution Upscaling: It boosts video content ranging from 360p to 1440p up to your display’s native resolution (e.g., upscaling 1080p to 4K), making both streaming and local video files appear much sharper.
- AI Artifact Removal & Denoising: Crucially, the AI model actively analyzes and eliminates common streaming defects, such as the distracting macro-blocking (color blocks) and general video noise or graininess.
B. RTX Video HDR
RTX Video HDR is a powerful complementary feature that focuses on color, light, and contrast.
The vast majority of online content is delivered in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR), which offers limited brightness and color depth. Video HDR uses a separate AI model to analyze SDR content frame-by-frame and intelligently convert the color and brightness values to meet the High Dynamic Range (HDR) standards.
It converts SDR video content in real-time into the HDR10 format. When viewed on an HDR-compatible display, this results in dramatically more vivid colors, deeper shadows, and brighter, more realistic highlights.
System Requirements at a Glance
To utilize the full potential of both VSR and Video HDR, users must meet the following criteria:
Hardware: GeForce RTX 30-Series or 40-Series GPUs (or newer). While some older RTX cards may support certain features, the 30-Series and newer provide the best, most reliable experience for the full suite of enhancements.
Software: The latest NVIDIA GeForce Game Ready Driver is mandatory, as it contains the required AI models and settings.
Supported Applications: VSR and HDR are currently supported by:
- Major Chromium-based browsers, including Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge.
- Specific Video Players that have integrated the RTX Video SDK, such as VLC Media Player.
RTX VSR Application Scenarios: Where AI Transforms Your Viewing
RTX Video Enhancement is designed to be a "set it and forget it" tool that passively improves video quality across your PC, tackling common visual shortcomings in both streaming and locally stored content.
Here are the primary scenarios where VSR and Video HDR shine, instantly delivering a higher-quality image:
A.Real-Time Streaming and Online Content
The most common application for RTX Video is improving the viewing experience on major online platforms, which often use heavy compression to save bandwidth.
- YouTube and General Web Video: When viewing videos uploaded in 720p or 1080p, VSR automatically kicks in to upscale the content to match your high-resolution monitor (e.g., 4K or 1440p). This eliminates the blurriness that results from simple browser stretching.
- Live Streams and Gaming VODs (Twitch/YouTube Gaming): Live streaming often utilizes highly compressed video formats minimize latency. VSR and its Denoising function are particularly effective here, cleaning up the chunky macro-blocking and noise that commonly plague low-bitrate streams, making gaming action look much clearer.
- Subscription Services (Netflix, Hulu, Disney+): Even if you are subscribed to a plan that doesn't offer 4K streaming, or if your network bandwidth dips, VSR can take the 1080p or 720p stream and enhance it closer to a native high-resolution presentation.
B. Local Video Playback and Archival Content
Thanks to integration with video players like VLC and through the RTX Video SDK, VSR is not limited to web browsers. It can dramatically improve your library of older video files.
- Upscaling Older Movies and TV Shows: If you have an archive of media ripped from DVDs or older Blu-rays (often 480p or 720p), VSR can upscale this content to your modern display’s native resolution. This breathes new life into classic content, adding details that were previously lost during standard playback scaling.
- Home Videos and Personal Archives: VSR is a great solution for digitizing and viewing older home video footage or clips recorded on dated equipment (which often suffer from severe noise and low resolution).
- Enhancing SDR Content with HDR: For all the above scenarios, if the source video is SDR, RTX Video HDR can activate automatically (provided you have an HDR-compatible display) to inject greater color vibrancy and contrast, making older content pop off the screen.
In short, wherever the original video quality is lower than your display's resolution, or wherever video compression has introduced visual artifacts, RTX Video Enhancement is there to provide an immediate, AI-driven visual upgrade.
How to Turn on RTX Video Enhancement
Enabling RTX Video Enhancement is straightforward and requires just a few clicks within the NVIDIA Control Panel. Once enabled, the technology works automatically in the background, applying AI upscaling whenever you play supported video content.
Follow these steps to activate both RTX Video Super Resolution (VSR) and RTX Video HDR:
Step 1: Confirm Driver and Hardware Readiness
Before starting, ensure your system meets the basic requirements:
- GPU: Verify you are using a GeForce RTX 30-Series or newer graphics card.
- Driver: Download and install the very latest GeForce Game Ready Driver from the NVIDIA website or GeForce Experience application. The latest driver is crucial as it contains the most recent AI models and stability fixes.
Step 2: Access NVIDIA Control Panel Settings
- Open the NVIDIA Control Panel: Right-click on your desktop and select "NVIDIA Control Panel."
- Navigate to Video Settings: In the left-hand menu, under the Video category, click on Adjust video image settings.
Step 3: Activate Super Resolution (VSR)
In the "Adjust video image settings" window, click on the RTX Video Enhancement tab (usually the second tab from the left).
- Enable VSR: Check the box next to Super Resolution.
- Select Quality Level: Once enabled, you must choose a quality level between 1 (Lowest Quality, Lowest Performance Impact) and 4 (Highest Quality, Highest Performance Impact).
- Level 1: Recommended for older RTX 30-Series cards or systems with lower power limits.
- Level 4: Recommended for higher-end RTX 40-Series cards to maximize visual fidelity.
- Tip: Start with Level 2 or 3 for a good balance of performance and quality, and adjust if you notice any frame drops or excessive heat.
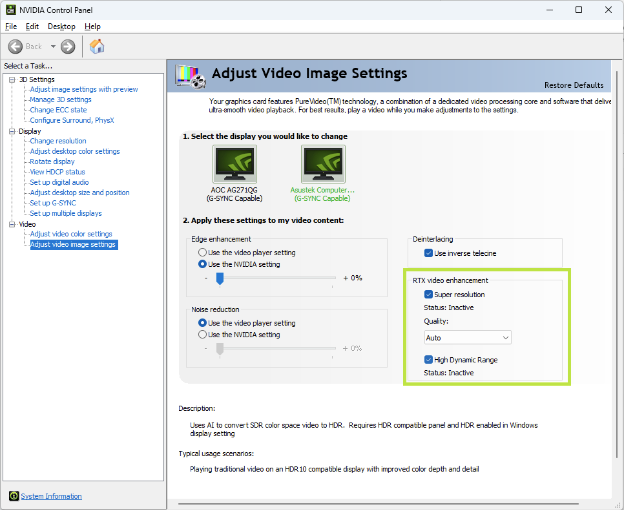
Step 4: Enable RTX Video HDR (Optional)
If you have an HDR-compatible monitor and have HDR enabled in Windows Display Settings, you can also activate the HDR enhancement:
- Enable HDR: Check the box next to High Dynamic Range.
- Verify Windows HDR: Ensure Windows HDR is toggled ON in your system’s display settings for this feature to work correctly.

Step 5: Start Playback in a Supported Application
With the settings saved, you are ready to go. Simply open one of the supported applications and start playing a video:
- Browsers: Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge.
- Video Players: VLC Media Player (ensure it is the latest version that supports the RTX Video SDK).
VSR will automatically apply the upscaling and denoising to any video stream or file that is within the supported resolution range (360p to 1440p), transforming your viewing experience immediately.
Troubleshoot Common VSR Questions
While RTX Video Enhancement is designed to be seamless, users often encounter specific questions regarding performance, compatibility, and why the feature might not be activating. Here are answers to the most frequently asked questions and solutions for common issues.
Q1: Why is VSR active, but the video quality hasn't changed?
This is the most common issue. VSR is subtle, but if you see no change, check these factors:
- Resolution Check: VSR only activates when the video's resolution is within the supported range: 360p (or higher) up to 1440p. If the video is 240p (too low) or native 4K (too high), VSR will skip the process. Ensure you have selected a low-to-mid resolution on the streaming platform (e.g., 720p or 1080p) for VSR to work its magic.
- Browser Overrides: Ensure your browser is not being explicitly forced to use a different scaling method. For Chrome or Edge, make sure hardware acceleration is enabled in the rowser settings.
- Full-Screen Requirement: VSR often works best and is most noticeable when the video player is taking up a significant portion of the screen or is in full-screen mode.
- Driver and System: Double-check that your GeForce Game Ready Driver is the latest version and that VSR is correctly toggled on (Level 1-4) in the NVIDIA Control Panel.
Q2: How much GPU performance and power will VSR consume?
VSR is not free; it utilizes your GPU's Tensor Cores, adding to the overall load and power draw of your system.
- Performance Impact: The usage depends heavily on the Quality Level you select (Level 1 is lowest impact, Level 4 is highest) and the complexity of the video. High-quality levels applied to low-resolution video (e.g., 480p upscaled to 4K) will require the most power.
- Best Practice: NVIDIA designed VSR to run efficiently. For most users, Level 2 or 3 offers an excellent balance between visual gain and performance cost. If you find your GPU overheating or your game frame rates dropping while streaming on a secondary monitor, lower the VSR quality level. It is generally recommended to only use VSR when you are not simultaneously running demanding 3D games.
Q3: VSR doesn't work in my favorite browser (like Firefox) or older media player. Why?
RTX Video Enhancement is not a universal Windows feature; it requires explicit integration.
- API Dependency: VSR relies on specific, low-level integration with the video decoding pipeline, which is primarily supported by the APIs in Chromium-based applications.
- Compatibility Reality: Currently, official support is confined to Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and modern versions of VLC Media Player that have integrated the necessary SDK. Other browsers or media players must adopt the NVIDIA SDK to gain VSR functionality.
Q4: Why is my video flickering or flashing when VSR is on?
If you experience flickering or flashing (especially with older video formats or when HDR is active), it may be a compatibility conflict:
- HDR Conflict: Temporarily disable RTX Video HDR in the NVIDIA Control Panel to isolate the issue. If the flickering stops, the conflict is with your monitor's or Windows' HDR implementation.
- Video Playback: Ensure the video player's rendering settings are compatible with VSR. For extreme cases, a simple driver clean install or rollback might be necessary.
RTX VSR's Inherent Limitations and The Need for Professional Tools
RTX Video Enhancement is an incredible tool for instantaneous viewing improvement, yet its real-time nature imposes certain technical boundaries. For users who demand the absolute highest quality, permanent results, or support for legacy content, VSR's limitations become apparent.
Understanding these boundaries is crucial for identifying when a more powerful, professional solution is required.
Limitation 1: Real-Time-Only – No Permanent File Output
VSR processes the video stream as it is being played and discarded. This is its most significant limitation.
The enhanced video is only visible on your screen at that moment. You cannot save the upscaled, noise-reduced version as a new video file to keep, share, or use in other projects (like video editing software).
If you want to permanently enhance an entire movie, a collection of old home videos, or a favorite downloaded clip, VSR cannot help—it is purely a viewing solution.
Limitation 2: Sub-Par Performance on Severely Degraded Sources
While VSR excels at removing common compression artifacts (macro-blocking), its real-time constraint limits its ability to repair truly broken or low-quality content.
VSR utilizes a single frame or a very small group of frames to perform its analysis in milliseconds. This is often insufficient for severe issues like:
- Heavy Motion Blur and Judder: The AI lacks the "look-ahead" capability to properly reconstruct complex or rapidly moving details.
- VHS/DVD Level Degradation: It struggles with the deep noise, severe chroma bleed, and interlace artifacts common in decades-old analog footage.
For professional archival, restoration, or enhancing deeply compressed content (e.g., from old digital cameras), VSR provides only a minor improvement, as it cannot perform the intensive, multi-pass analysis required for true restoration.
Limitation 3: Strict Hardware and Application Dependency
The technology is locked into the NVIDIA ecosystem.
RTX VSR requires a GeForce RTX 30-Series or newer GPU and is limited to specific supported applications (Chrome, Edge, VLC).
Users without a high-end NVIDIA card, or those working in environments that prohibit the use of specific browsers or players, simply cannot access the enhancement, regardless of their content needs.
Address the Limitations
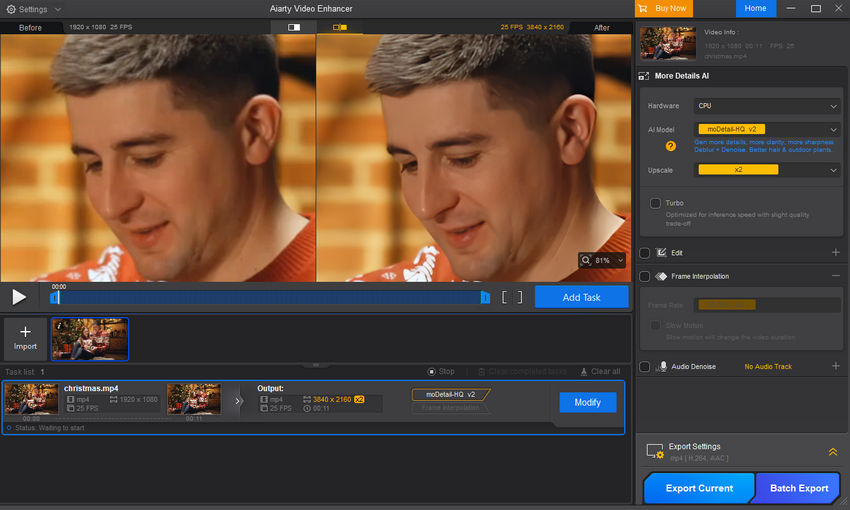
If your needs go beyond real-time playback—if you're looking to permanently repair and save your enhanced videos with the highest possible detail—you need a dedicated, professional AI enhancement application. One of the best AI video enhancers is Aiarty Video Enhancer.
Aiarty can address the core limitations of real-time tools like VSR. It acts as a full-service digital restoration studio for your media library:
- Permanent File Output: Unlike VSR, Aiarty processes your video offline, allowing it to use the full power of your GPU without worrying about real-time speed. The result is a brand new, saved video file (up to 4K), ready for archiving, sharing, or professional use.
- Deep, Specialized Restoration: Aiarty uses advanced multi-frame analysis and features specialized AI models for different content types. This deeper approach fixes severe issues that VSR can't handle in real-time, such as heavy noise, complex motion blur, and damage from old analog sources.
- Flexible Platform Support: Aiarty isn't strictly limited to a specific NVIDIA hardware generation. This gives all users seeking professional results greater flexibility and control over the enhancement process, regardless of their exact GPU setup.
You click the button to download and test it with your own video library!
Conclusion
RTX VSR is a fantastic, convenient upgrade for your everyday viewing. But when the goals shift to preservation, deep restoration, and permanent, high-fidelity output, Aiarty Video Enhancer is the necessary professional tool to truly unlock the potential of your video library.